National Center for Learning Disabilities (NCLD). (2017). The effectiveness of Tier 2 and Tier 3 RTI interventions: A meta-analysis. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6701471/
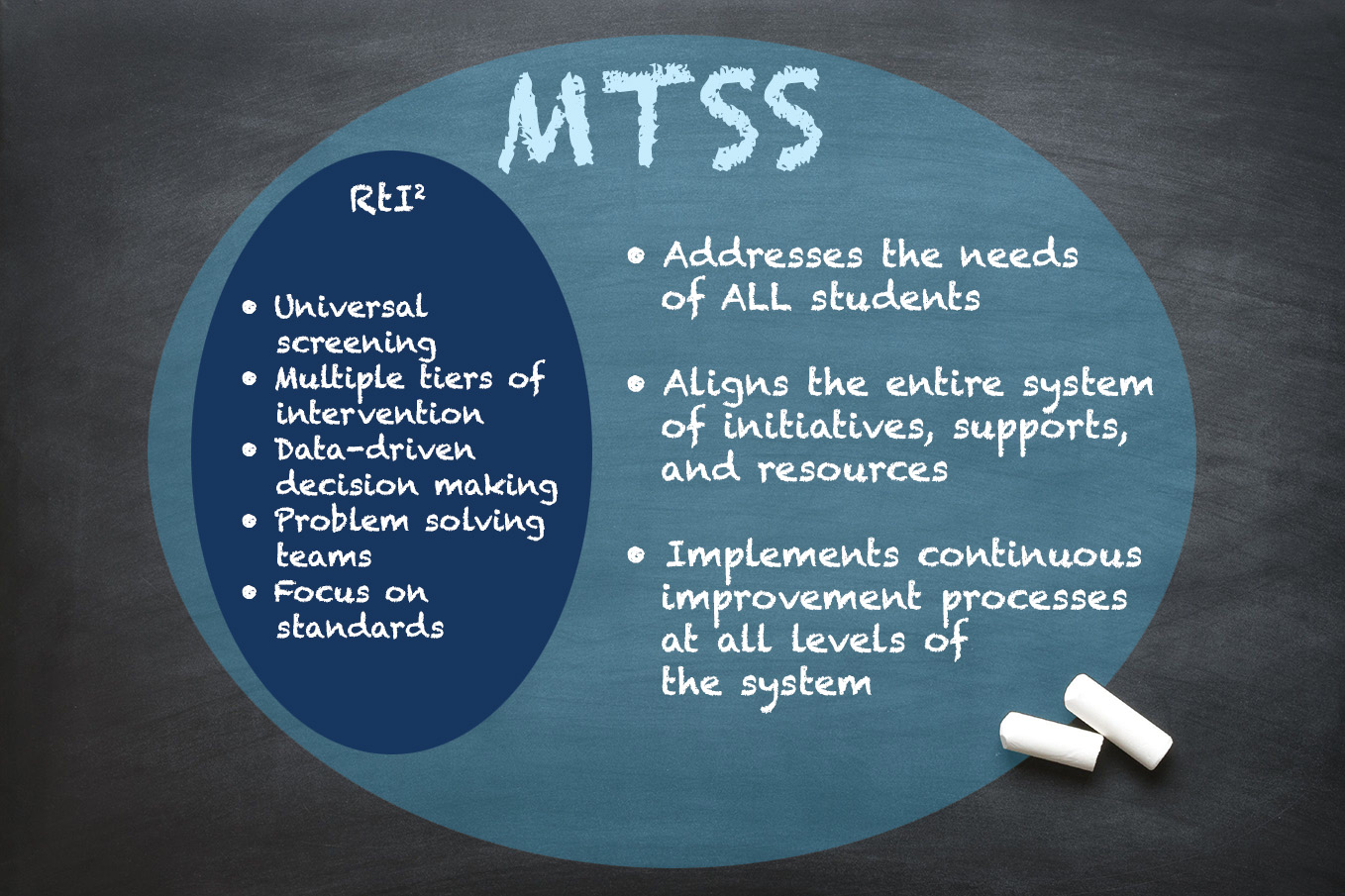
A 2017 meta-analysis by the National Center for Learning Disabilities (NCLD) found that students who received Tier 2 and Tier 3 RTI interventions made significantly greater gains in reading achievement than students who did not receive these interventions. Both Response to Intervention (RTI) and Multi-Tiered Systems of Support (MTSS) aim to support struggling students with research-based interventions, but they differ in their scope and approach to intervention.
The Importance of Implementing MTSS
Implementing a multi-tiered system in education is crucial for meeting the diverse needs of students and ensuring their academic success. This tiered approach allows for targeted interventions and support at different levels, based on students’ requirements. MTSS is a broader framework that encompasses RTI but also includes a wider range of supports beyond academics, such as behavioral and social-emotional interventions.
By implementing a multi-tiered system, educators can identify and address the specific needs of students at various levels of proficiency. This tailored approach helps prevent students from falling through the cracks and ensures that all students receive the support they need to thrive academically. MTSS allows educators to provide early intervention for students who may be struggling academically. Additionally, MTSS allows for the differentiation of instruction, providing opportunities for both enrichment and additional support for students at different proficiency levels.

What Is RTI?
RTI is an evidence-based system of educational support for students with learning disabilities to help them achieve academic goals. It involves systematic progress monitoring and monitoring of student progress, providing evidence-based interventions as needed. The goal of RTI is to prevent academic failure and provide early support for students who are struggling.
At its core, RTI is about being proactive rather than reactive. Instead of waiting for a student to fail before offering assistance, RTI strives to identify students who are at risk for academic difficulties and provide targeted interventions to address their needs. This approach allows educators to address the individual needs of each student and give the necessary support to help them succeed.
Explanation of the RTI framework
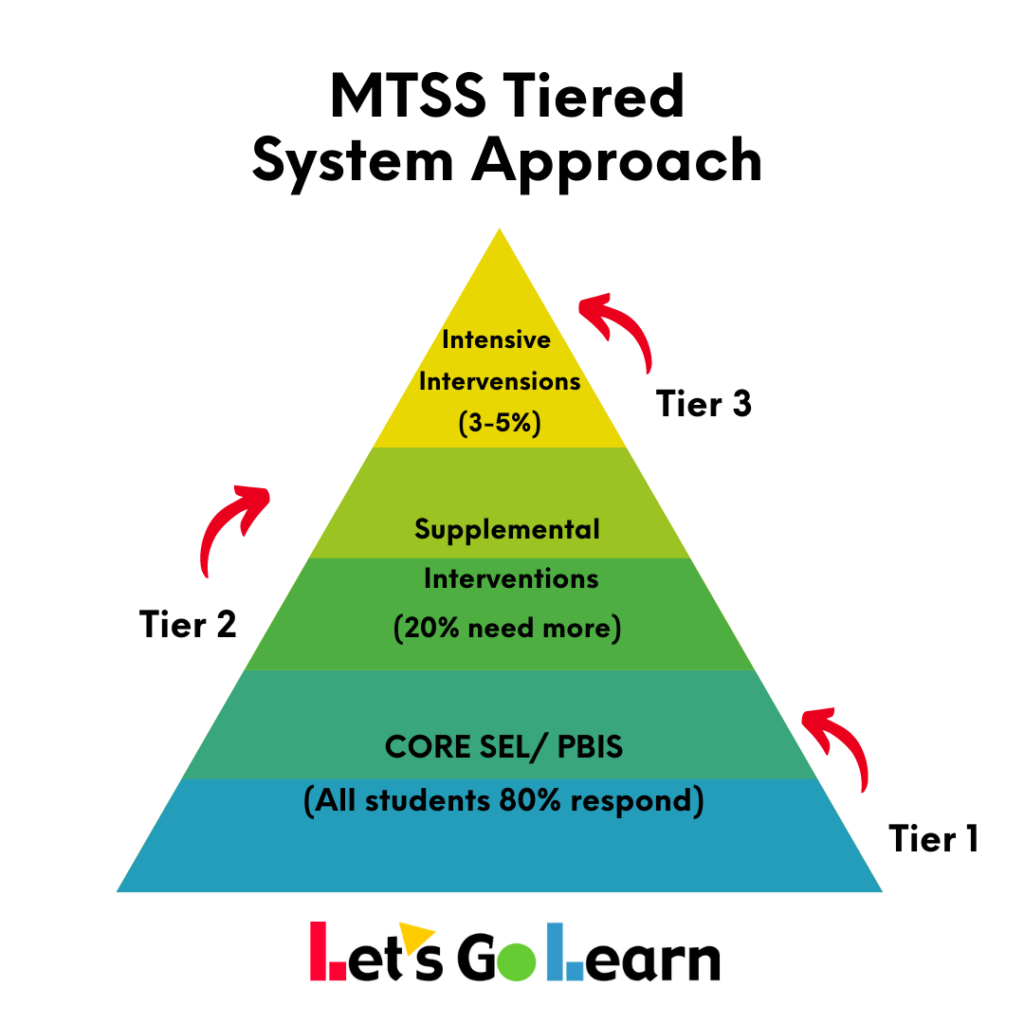
RTI typically consists of three tiers of support. Tier 1 involves universal interventions that are provided to all students, such as high-quality classroom instruction and school-wide behavior support. Tier 2 consists of targeted interventions for students who require additional support, such as small-group instruction or individualized assistance. Tier 3 involves intensive interventions for students who continue to struggle despite Tier 1 and Tier 2 interventions.
Understanding Response to Intervention (RTI)
One of the key components of RTI is the use of data to inform decision-making. By regularly monitoring student progress and analyzing assessment data, educators can identify students who are not making adequate progress and provide the appropriate interventions to address their specific needs. This data-driven approach allows educators to make informed decisions about the effectiveness of interventions and make adjustments as needed. RTI is a comprehensive approach to identifying and supporting struggling learners. By providing early and targeted interventions, educators can help prevent academic failure and support students in reaching their full potential.
Benefits of Using RTI
RTI is a popular approach used in schools to help support students who are struggling academically or behaviorally. This tiered support system provides targeted interventions based on students’ individual needs and progress. There are several benefits to using RTI in schools, including improved student outcomes, early identification of learning difficulties, and increased collaboration among educators. By providing targeted interventions and support, educators can help struggling students catch up to their peers and achieve success. Research has shown that RTI can lead to significant improvements in students’ reading and math skills, as well as reduce problem behaviors. By regularly screening students for academic and behavioral concerns, educators can identify struggling students early on and give them the help they need. This early intervention can prevent students from falling further behind and help them get back on track.
Early Identification and Intervention for Struggling Learners
In education, one of the most important ways to support student success is through the early identification of struggling learners, accompanied by effective intervention. By recognizing students who are facing challenges early on, educators can provide targeted support and interventions to help them catch up and thrive. This proactive approach not only prevents students from falling further behind but also sets them up for future success by addressing their needs promptly.
Challenges of Implementing RTI
Implementing RTI in schools can be challenging. While the ultimate goal of RTI is to improve student outcomes, there are several hurdles that educators may face when trying to implement this framework effectively.
One of the main challenges of implementing RTI is the need for significant resources, including time, money, and personnel. To provide appropriate interventions for all students, schools must have the necessary staff and materials to assess, monitor, and support student progress. RTI requires a high level of collaboration and coordination among educators, administrators, and support staff. This can be difficult to achieve in schools where there may be competing priorities and a lack of a unified vision for student success. It takes time and effort to establish clear communication channels, shared goals, and a consistent approach to implementing interventions.
Lack of Resources and Support
Another challenge of RTI is the need for ongoing professional development and training for educators. This is essential to making sure teachers have the knowledge and skills to effectively assess student needs, plan and implement interventions, and monitor progress. Without adequate training, there is a risk that interventions will not be implemented with commitment, leading to ineffective support for struggling students.
The process of data collection and analysis required for RTI can be overwhelming for educators. It is essential to gather and analyze data on student performance to determine the effectiveness of interventions and make informed decisions about the next steps. This requires a significant amount of time and effort, which can be a challenge for educators who already have demanding workloads.

Let’s Go Learn is an education company specializing in data-driven assessments and tools to support educators in implementing Response to Intervention (RTI). Let’s Go Learn’s products address the burden of data collection and analysis in RTI by:
- Automating assessment: Let’s Go Learn offers diagnostic assessments in reading and math (DORA and ADAM) that can be administered online. These adaptive assessments pinpoint specific student skill gaps, reducing the need for educators to design and administer their own tests.
- Making data-driven recommendations: Based on the assessment results, Let’s Go Learn can provide educators with data reports and recommendations for targeted interventions aligned with individual student needs. This saves educators time spent analyzing data and deciding on the next steps.
- Monitoring progress: Let’s Go Learn allows for ongoing progress monitoring to track student response to interventions. This eliminates the need for educators to manually collect and analyze data throughout the RTI process.
Let’s Go Learn’s focus on automation and data-driven recommendations can lighten the workload for educators implementing RTI, allowing them to focus on delivering effective interventions.
Feeling Overwhelmed by RTI? There's a Better Way.
Let’s Go Learn takes the burden off your shoulders. Streamline your RTI process with automated assessments, data analysis, and progress monitoring.
Fidelity of Implementation
Fidelity of implementation is an important concept in education that relies on using evidence-based practices. It refers to the degree to which an intervention or program is being implemented as intended by the developers. In other words, it measures how closely the actual implementation matches the original design and goals of the intervention.
Fidelity of implementation is essential because it directly impacts the effectiveness of the intervention. If a program is not being implemented as it was originally designed, it is unlikely to produce the intended outcomes. In education, if a teacher does not follow the specific strategies and guidelines outlined in a reading intervention program, that program is less likely to be successful in improving students’ reading skills. Fidelity of implementation can be measured through various methods, such as observations, self-reports, and fidelity checklists. It is not a one-time event but rather a continuous process throughout the implementation of the intervention. This requires ongoing training and supervision to ensure that implementers have the necessary skills and support to deliver the intervention with fidelity.
What Is MTSS?
MTSS, or Multi-Tiered System of Support, is a comprehensive framework that schools use to support the academic, behavioral, and social-emotional needs of all students. This approach involves implementing a range of evidence-based practices and interventions to ensure that all students receive the level of support they need to succeed.
At its core, MTSS is based on the belief that all students can learn and achieve, but they may need different levels of support to do so. This framework emphasizes early intervention and prevention, as well as ongoing progress monitoring to identify students who may be struggling and provide them with targeted support. MTSS also takes into account the diverse needs of students, recognizing that one-size-fits-all approaches are insufficient for meeting the wide range of needs seen in schools today.
Exploring Multi-Tiered System of Supports (MTSS)
MTSS typically comprises three tiers of support. The first tier, known as Tier 1, involves universal, school-wide supports that are available to all students. These may include high-quality instruction, positive behavior support, and social-emotional learning programs. Tier 2 involves targeted support for students who require additional help beyond what is provided in the universal tier. This may include small-group interventions, mentoring, or counseling. Finally, Tier 3 provides intensive individualized support for students who continue to struggle despite the support in place at Tiers 1 and 2.
Overview of the MTSS Framework
At its core, MTSS is built on the principles of providing early intervention, using data to inform decision making, and implementing evidence-based practices. One of the key components of MTSS is the use of data to guide decision making at each tier. This data-driven approach allows educators to identify students who are at risk for academic or behavioral difficulties and monitor their progress over time. By analyzing this data, educators can make informed decisions about the types and intensity levels of intervention that are most appropriate for each student.
MTSS also emphasizes the importance of collaboration among educators, parents, and other stakeholders in supporting student success. This collaborative approach ensures that students receive a continuum of support across multiple settings, including the classroom, school, and home.
Overall, the MTSS framework is intended to help schools create a responsive system of support that meets the needs of all students. By providing a continuum of evidence-based interventions and using data to guide decision making, MTSS aims to improve academic and behavioral outcomes for all students.


Leave A Comment